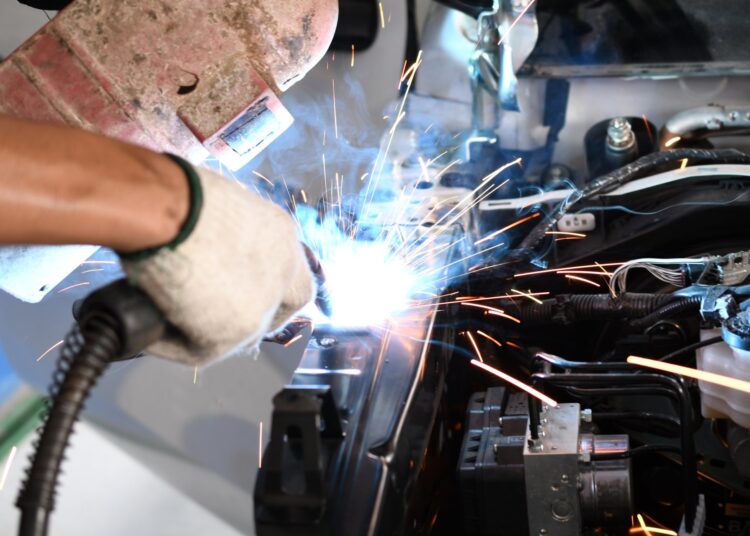
Choosing the right materials for an automotive welding project goes far beyond just picking a piece of metal. The materials selected influence the vehicle’s safety, longevity, and overall performance. Understanding why material selection matters in automotive welding helps technicians produce quality, lasting repairs.
For anyone involved in automotive work, from seasoned professionals to weekend hobbyists, grasping these concepts builds a foundation for success.
Weld Strength and Durability Depend on Materials
The choice of base metals and filler materials directly impacts the strength of a welded joint. For instance, welding high-strength steel requires a specific filler metal that matches its properties to maintain structural integrity.
Using an incorrect filler can create a weak point that compromises the vehicle’s frame, especially under the stress of a collision. A durable weld resists fatigue and corrosion over time, contributing to the vehicle’s overall lifespan.
Material Selection Impacts Weight and Efficiency
Automakers continuously seek ways to make vehicles lighter to improve fuel economy. This has led to the increased use of materials like aluminum and advanced high-strength steels (AHSS). Welding these materials presents unique challenges. Aluminum, for example, dissipates heat quickly and requires a different technique than steel.
Choosing the right lightweight materials and welding processes allows us to create strong, reliable joints without adding extra weight, which helps keep the vehicle’s fuel efficiency on track.
Corrosion Resistance Begins with the Right Materials
Vehicles face constant exposure to moisture, road salt, and other corrosive elements. The materials used in welding repairs can either help prevent or accelerate rust and degradation.
Selecting materials with inherent corrosion-resistant properties, like certain grades of stainless steel or properly coated metals, is a protective measure. When welding, it’s also important that the filler material has compatible corrosion resistance to the base metal to prevent galvanic corrosion, where one metal corrodes faster than another.
Safety and Crashworthiness Relies on Proper Material Use
A vehicle’s ability to protect its occupants during a crash depends on the structural integrity of its components. Many parts of a modern car frame are designed to crumple in specific ways to absorb impact energy.
Using the wrong type of material in a repair can alter these crumple zones, potentially changing how the vehicle behaves in an accident. The role of welding in the automotive industry extends to preserving these safety features, and that begins with the correct material selection.
The Right Material Guides the Welding Technique
Different materials have different properties, such as melting points and thermal conductivity, which dictate the welding process required.
- Steel: Often welded using MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding for its speed and efficiency.
- Aluminum: Typically requires TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding or a specialized MIG setup with a spool gun because of its lower melting point and high thermal conductivity.
Understanding why choosing the proper materials for automotive welding matters helps a technician select the right equipment and technique, leading to cleaner, stronger, and more reliable welds. By carefully considering the materials for each job, welders can produce work that meets safety standards and contributes positively to vehicle performance.